ü Significance of Lysosomes
1 In WBC or
leucocyte: Cell of leucocyte digest foreign protein, bacteria and viruses.
2.
In
autophagy: During starvation, the lysosomes digest stored food contents
such as proteins, fats and glycogen of the cytoplasm and supply the necessary
amount of energy to the cell.
3.
In
metamorphosis (Frog): During the transformation of a tadpole into frog, the
embryonic tissues such as gills and tails are digested by the lysosomes and
utilized by other body cells.
4.
In
Fertilization: The lysosomal enzymes present in the acrosome of sperm cells
digest the limiting membrane of the ovum (egg) Thus, the sperm cell is able to
enter the ovum and start the fertilization.lysosome information
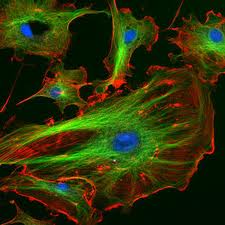
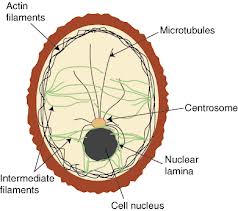
ü Cytoskeleton
Recently complex networks of fibrous protein structures have
been shown to exist in the cytosol of eukaryotic cell. These networks
collectively form cytoskeleton, which
contains three types of protein fibres:
1.
Microtubules(of tubulin protein),
2.
Microfilaments(of actin protein),
3.
Intermediate Filaments (of Keratin and other
types of protein).
These
fibrous proteins help in cellular movement i.e., amoeboid movement and
cyclosis. They also help the cells to maintain their shapes.cytoskeleton
ü Significance of Diploidy
Diploid state of organism is originated during process of
fertilization of sexual reproduction. During fertilization, two haploid cells
or gametes of different types: sperm of man and ovum of women are fused together
to form a diploid egg (zygote). This egg divides by mitotic cell divisions to
form numerous diploid body cells, making the body of diploid organism.
ü Cell Terms
1. Protoplasm: The contents of a living
cell, contained within the plasma membrane, form protoplasm. Protoplasm is
usually differentiated into the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
2. Gene:
It is a distinct unit of
hereditary information. Gene is inherited from one generation to next and
determines an observable characteristic or trait of an organism. Genes have to
carry coded information of parents to their children or progeny, so that
children remain exactly like their parents. Generally a gene is made up of DNA
molecule, but sometimes it is made up of RNA molecule as observed in Tobacco
Mosaic Virus(TMC)
3. DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid; a polymeric
nucleic acid.
4.
RNA:
Ribonucleic acid; a polymeric nucleic acid.
.
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
No comments:
Post a Comment